Are you curious about what a nuclear stress test is and how long it takes? In this article, we will provide you with all the information you need. A nuclear stress test is a medical procedure used to evaluate the blood flow to your heart. It can help doctors diagnose heart conditions, such as coronary artery disease. We will explain the purpose of the test, how it works, and the different types available. Stay tuned to find out how to prepare and what to expect during this test.
What Is a Nuclear Stress Test
To understand what a nuclear stress test is, you will need to go through a procedure that involves the injection of a small amount of radioactive substance into your body. This test is used to evaluate the blood flow to your heart and detect any abnormalities or blockages in the coronary arteries. The benefits of a nuclear stress test include its ability to provide valuable information about the functioning of your heart and help diagnose conditions such as coronary artery disease. It can also help determine the effectiveness of any treatments you may be undergoing.
One thing to consider when getting a nuclear stress test is the cost. The cost of a nuclear stress test can vary depending on factors such as the location, the facility, and any additional services or tests that may be required. It is important to check with your insurance provider to determine if the test is covered, and if so, what portion of the cost you will be responsible for. Some insurance plans may require prior authorization before the test can be performed. It is also worth noting that while the cost of a nuclear stress test may be a concern for some individuals, the benefits of the test in terms of diagnosing and managing heart conditions can outweigh the financial considerations.
Why would a cardiologist order a nuclear stress test
The purpose of a nuclear stress test is to assess the blood flow to your heart and detect any abnormalities or blockages in the coronary arteries, providing valuable information about your heart’s functioning and aiding in the diagnosis of conditions such as coronary artery disease. This test is commonly used by doctors to evaluate the overall health of your heart and determine the best course of treatment for any detected issues. Some benefits of a nuclear stress test include:
- Accurate assessment: The test helps in accurately assessing the blood flow to your heart, allowing doctors to identify any areas of reduced blood supply or blockages in the coronary arteries.
- Early detection: By detecting abnormalities or blockages at an early stage, a nuclear stress test can help doctors initiate appropriate treatment measures promptly, potentially preventing further damage to your heart.
- Tailored treatment plan: The information obtained from the test aids in developing a personalized treatment plan specific to your heart condition, ensuring you receive the most effective care.
- Monitoring progress: For individuals with known heart conditions, a nuclear stress test can be used to monitor the effectiveness of ongoing treatments and interventions, helping doctors make necessary adjustments when needed.
- Risk assessment: The test also provides valuable information about your risk of developing heart-related complications, allowing healthcare professionals to take preventive measures and manage your heart health more effectively.
Despite its numerous benefits, it is important to be aware of the limitations of a nuclear stress test, which include:
- False positives: In some cases, the test may indicate an abnormality or blockage that is not actually present, leading to unnecessary anxiety and further invasive procedures.
- False negatives: On the other hand, there is also a possibility of the test failing to detect a true abnormality or blockage, potentially delaying necessary treatment.
- Radiation exposure: The test involves the administration of a small amount of radioactive material, which exposes you to a minimal amount of radiation. While the risk is generally low, it is still important to consider the potential long-term effects, especially for individuals who require repeated testing.
It is crucial to discuss the potential benefits and limitations of a nuclear stress test with your healthcare provider to make an informed decision about whether the test is appropriate for your specific situation.
How Does a Nuclear Stress Test Work
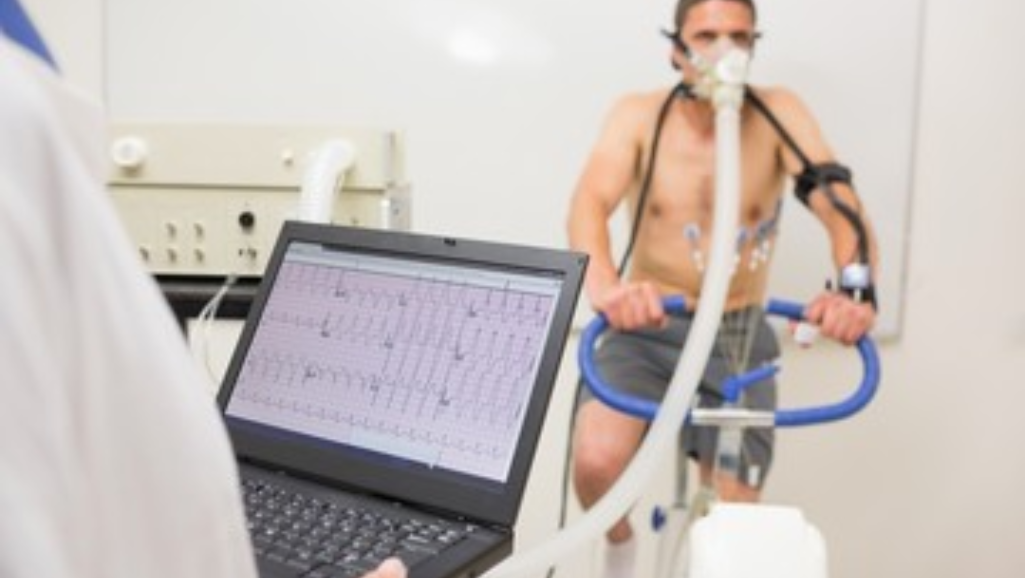
Assessing the blood flow to your heart and detecting any abnormalities or blockages in the coronary arteries, a nuclear stress test works by using a small amount of radioactive material to provide valuable information about your heart’s functioning. During the nuclear stress test procedure, you will be given a radioactive tracer, usually through an injection or through a small amount of radioactive material that you inhale or swallow. This tracer travels through your bloodstream and is detected by a special camera called a gamma camera. The gamma camera takes images of your heart at rest and during exercise or stress. By comparing these images, doctors can evaluate the blood flow to your heart muscle and identify areas where blood flow may be reduced or blocked.
The benefits of a nuclear stress test are numerous. It can help diagnose coronary artery disease, assess the severity of a heart condition, determine the effectiveness of heart treatments, and guide decisions regarding further diagnostic tests or treatment options. Additionally, the nuclear stress test can provide important information about the overall health of your heart and help identify any potential risks or complications. It is a non-invasive and relatively safe procedure, with minimal side effects and risks associated with the radioactive tracer. Overall, a nuclear stress test is a valuable tool that can provide crucial information about your heart’s functioning and help guide your healthcare provider in developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Types of Nuclear Stress Tests
When undergoing a nuclear stress test, you will encounter different types of tests to assess the blood flow to your heart and detect any abnormalities or blockages in the coronary arteries. These tests are designed to provide accurate and detailed information about your heart’s functioning and help your healthcare provider make an informed diagnosis. The different nuclear stress tests available include:
- Exercise stress test: This test involves walking on a treadmill or pedaling a stationary bike while your heart rate and blood pressure are monitored. It helps evaluate how well your heart functions during physical activity.
- Pharmacological stress test: If you are unable to exercise, this test is performed by injecting a medication into your bloodstream to mimic the effects of exercise on your heart. It helps assess your heart’s response to stress without physical exertion.
- Dual isotope stress test: This test involves the use of two different radioactive tracers to assess both the blood flow and heart function simultaneously. It provides a more comprehensive evaluation of your heart’s health.
- SPECT stress test: Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) is a type of nuclear stress test that uses a special camera to take images of your heart. It helps identify areas of reduced blood flow or damaged heart tissue.
- PET stress test: Positron emission tomography (PET) is another type of nuclear stress test that provides detailed images of your heart’s blood flow and metabolism. It can detect abnormalities in the heart muscle and help diagnose coronary artery disease.
The benefits of nuclear stress tests include their ability to accurately detect heart problems, determine the severity of blockages, assess the effectiveness of treatments, and guide further management decisions. These tests are safe and widely used in clinical practice to evaluate the health of your heart.
How do you prepare for a nuclear stress test
To prepare for a nuclear stress test, you should follow specific guidelines provided by your healthcare provider. The preparation steps for a nuclear stress test typically include dietary restrictions. Your healthcare provider will instruct you to avoid consuming any food or beverages that contain caffeine for at least 24 hours before the test. This includes items such as coffee, tea, chocolate, soda, and certain medications. Caffeine can interfere with the results of the test, so it is important to adhere to these restrictions.
In addition to avoiding caffeine, you may also be asked to refrain from eating or drinking anything for a certain period of time before the test. This is usually done to ensure accurate results and is typically around 4-6 hours prior to the test. Your healthcare provider will provide you with specific instructions regarding fasting and any necessary medication adjustments.
It is important to communicate with your healthcare provider about any medications you are currently taking, as they may need to be adjusted or temporarily discontinued before the test. Following these preparation steps and adhering to the dietary restrictions will help ensure accurate and reliable results from your nuclear stress test.
What to Expect During a Nuclear Stress Test
During a nuclear stress test, you will be monitored for any changes in your heart’s blood flow and function. This test is commonly used to determine if there are any blockages in your coronary arteries or if there are any areas of your heart that are not receiving enough blood supply. Here is what you can expect during a nuclear stress test:
- You will first be given a small amount of radioactive substance through an intravenous line. This substance helps to create images of your heart during the test.
- You will then be asked to either walk on a treadmill or receive medication that simulates the effects of exercise on your heart. This is done to increase your heart rate and blood flow.
- While you are exercising or receiving the medication, your heart’s activity will be monitored using an electrocardiogram (ECG) machine.
- After the exercise or medication is stopped, you will be given another dose of the radioactive substance. This allows for a comparison of the images taken during rest and exercise.
- Finally, a special camera will take images of your heart to evaluate the blood flow and function.
The nuclear stress test is highly accurate in diagnosing heart conditions, with a sensitivity of about 85% to 90%. As for side effects, they are generally rare and mild. Some individuals may experience chest discomfort, dizziness, or shortness of breath during the test. It is important to communicate any discomfort you may feel to the healthcare provider conducting the test.
How long does a nuclear stress take
The duration of a nuclear stress test typically ranges from 3 to 4 hours, allowing for thorough monitoring of your heart’s blood flow and function. This time frame includes both the rest and stress phases of the test. The average duration of the rest phase is around 30 minutes, during which you will receive an injection of a radioactive tracer and rest quietly while it circulates through your bloodstream. After this, you will undergo the stress phase, which can take anywhere from 2 to 3 hours. The timing considerations for this phase depend on the method used to induce stress. If you are exercising on a treadmill or stationary bicycle, the test will take longer compared to when a medication is used to simulate the effects of exercise. Additionally, factors such as your overall fitness level and any potential complications during the test can also impact the duration. It is important to follow any instructions given by your healthcare provider regarding medication use and dietary restrictions prior to the test to ensure accurate results.
Factors That Can Affect the Duration
Factors such as your age, medical history, and the presence of any underlying health conditions can influence the duration of a nuclear stress test. There are several factors that can affect how long the test takes and how accurate the results are:
- Physical fitness level: If you are physically fit, the test may take a shorter amount of time as your heart will be able to reach the necessary stress levels more quickly.
- Medications: Certain medications can affect the results of the test or require additional monitoring, which may extend the duration of the test.
- Body size: Larger individuals may require longer imaging times or additional scans to accurately evaluate the heart’s blood flow.
- Heart rate: If your heart rate is too high or too low during the test, it may be necessary to adjust the duration or intensity of the exercise, which can affect the overall test duration.
- Technical difficulties: Occasionally, technical issues such as equipment malfunction or poor image quality may arise, which can prolong the duration of the test.
It’s important to note that while a nuclear stress test is generally safe, there are potential complications that can occur. These include an allergic reaction to the radioactive tracer, abnormal heart rhythms, or chest pain. Your healthcare provider will closely monitor you throughout the test to ensure your safety.
Risks and Safety Precautions of a Nuclear Stress Test
To ensure your safety during a nuclear stress test, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and safety precautions involved. While nuclear stress tests are generally considered safe, there are some risks associated with the procedure. These risks can be minimized by following proper safety guidelines.
One of the main risks of a nuclear stress test is exposure to radiation. The amount of radiation used in this test is considered to be low and the benefits of the test usually outweigh the risks. However, it is still important to assess the risks and take necessary precautions.
Here are some safety guidelines to keep in mind during a nuclear stress test:
| Risk Assessment | Safety Guidelines |
|---|---|
| Radiation exposure | Limit unnecessary exposure by following proper shielding techniques and using the lowest possible dose of radiation. |
| Allergic reactions to the tracer | Inform your healthcare provider about any known allergies or sensitivities. They will take necessary precautions to minimize the risk of an allergic reaction. |
| Adverse side effects | Pay attention to any unusual symptoms during or after the test. Report them immediately to your healthcare provider. |
| Physical exertion | Follow the instructions given to you by your healthcare provider regarding exercise and physical exertion before and during the test. |
| Contrast dye used in some cases | If contrast dye is used, inform your healthcare provider about any history of allergies or kidney problems. They will monitor you closely for any adverse reactions. |
Interpreting the Results of a Nuclear Stress Test
When interpreting the results of a nuclear stress test, it is important for you to understand the implications and discuss them with your healthcare provider. The results of the test provide valuable information about the condition of your heart and can help guide your treatment plan. Here are some key points to consider when interpreting the results:
- Ischemia: The presence of ischemia indicates a reduced blood flow to the heart, which may be a sign of coronary artery disease.
- Infarction: Evidence of infarction suggests that there has been damage to the heart muscle, possibly due to a previous heart attack.
- Ejection fraction: This measures the percentage of blood that is pumped out of the heart with each beat. A low ejection fraction may indicate a weakened heart muscle.
- Wall motion abnormalities: Abnormal movement of the heart walls may suggest areas of the heart that are not receiving enough blood supply.
- Perfusion defects: These are areas of the heart that do not receive enough blood flow, which may be indicative of blocked or narrowed arteries.
Understanding the significance of these results is crucial in determining the appropriate course of action for your heart health. Your healthcare provider will be able to explain the findings in detail and recommend the most suitable treatment options based on the results of your nuclear stress test.
Follow-Up After a Nuclear Stress Test
After completing a nuclear stress test, it is important for you to schedule a follow-up appointment with your healthcare provider. This appointment is crucial because it allows your doctor to discuss the results of the test with you and develop an appropriate treatment plan if necessary.
During your follow-up appointment, your healthcare provider will go over the findings of the nuclear stress test and explain what they mean for your overall health. They will also provide you with any post-test instructions that you need to follow. These instructions may include dietary changes, medication adjustments, or recommendations for further testing or consultations with specialists.
It is also important to discuss any side effects or concerns that you may have experienced during or after the test. Your healthcare provider can address these issues and provide guidance on managing any discomfort or symptoms. They may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers, rest, or other strategies to help alleviate any side effects.
Remember to take note of any questions or concerns you have before your follow-up appointment so that you can discuss them with your healthcare provider. By following their post-test instructions and managing any side effects, you can ensure the best possible outcomes from your nuclear stress test.